
Problems are solved in the suitable spaces and coordinate systems
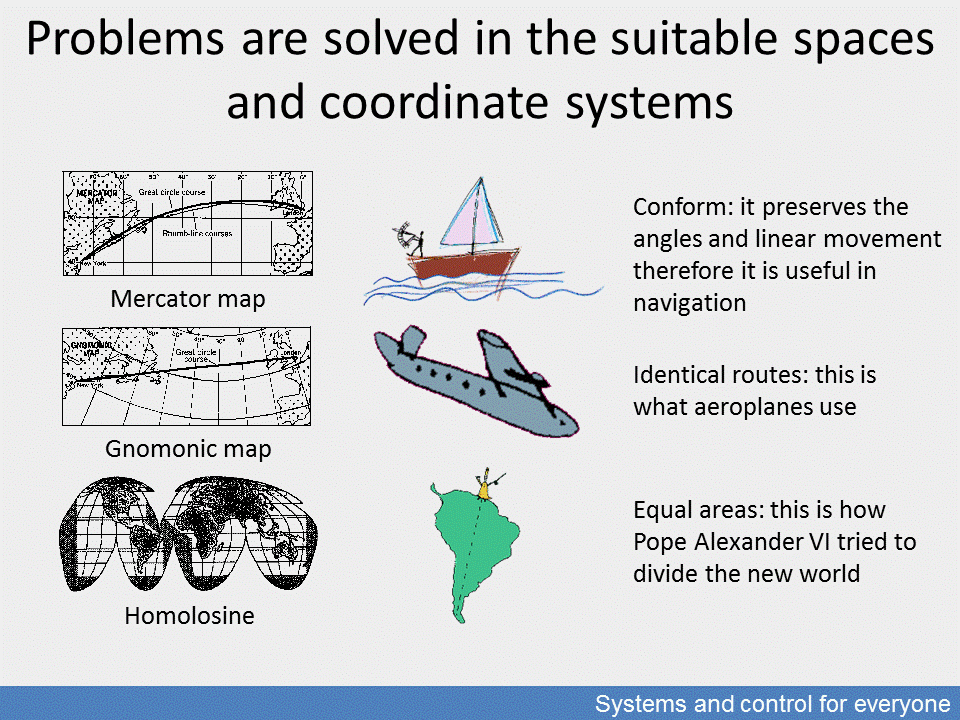
The relativity of dedicated representations, that is the space concept of a given problem, is best illustrated by the various geographical map representations serving various purposes. All maps represent space projected on a flat surface which overcomes the problem of the three-dimensional spherical shape of the Earth.
The most commonly used portrayal is the Mercator projection which helps traditional navigation by keeping directions constant. Gnomonic projection is used to find the shortest routes in aviation, and the Goode homolosine projection for portraying space in equal areas. The figure refers to how Pope Alexander VI divided the New World.
There are many projection types which focus on socio-economic identities and distort maps accordingly.