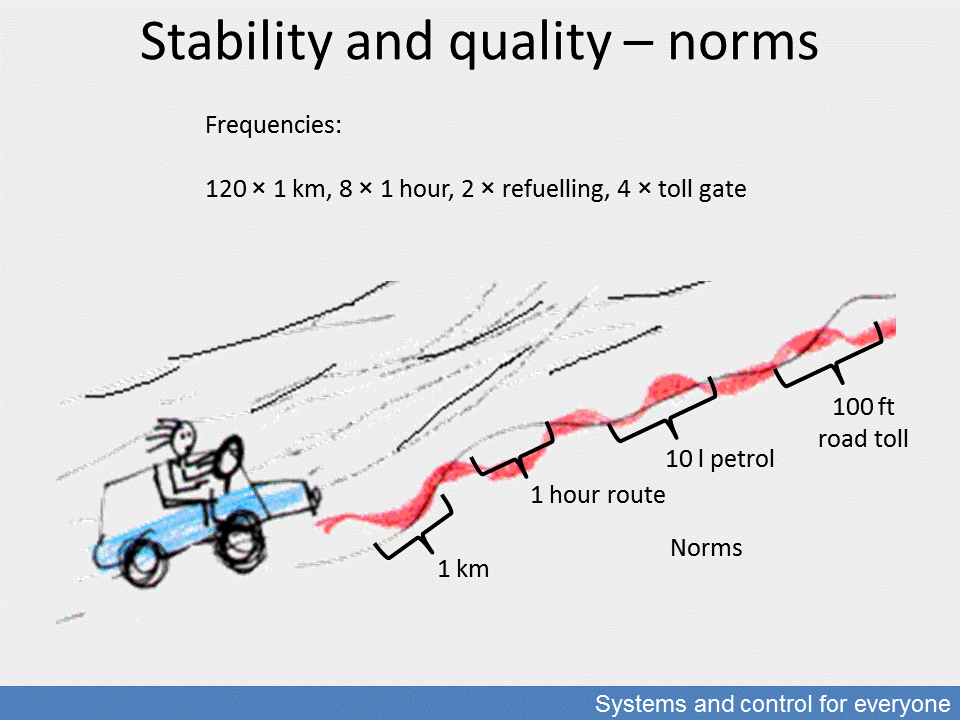

Stability and quality – norms
These functional equations are used to calculate the two main properties of controls: stability and compliance with quality requirements. Both are defined as measures on the trajectories described by the differential equation representing the process. The aim of control theory is to make these measures calculable and manipulable. All the mathematical concepts and methods discussed here serve this purpose. This is why control engineers tried to apply representations which can be easily matched both in the time domain and in the frequency domain, and can be used conveniently for solving the given problem.