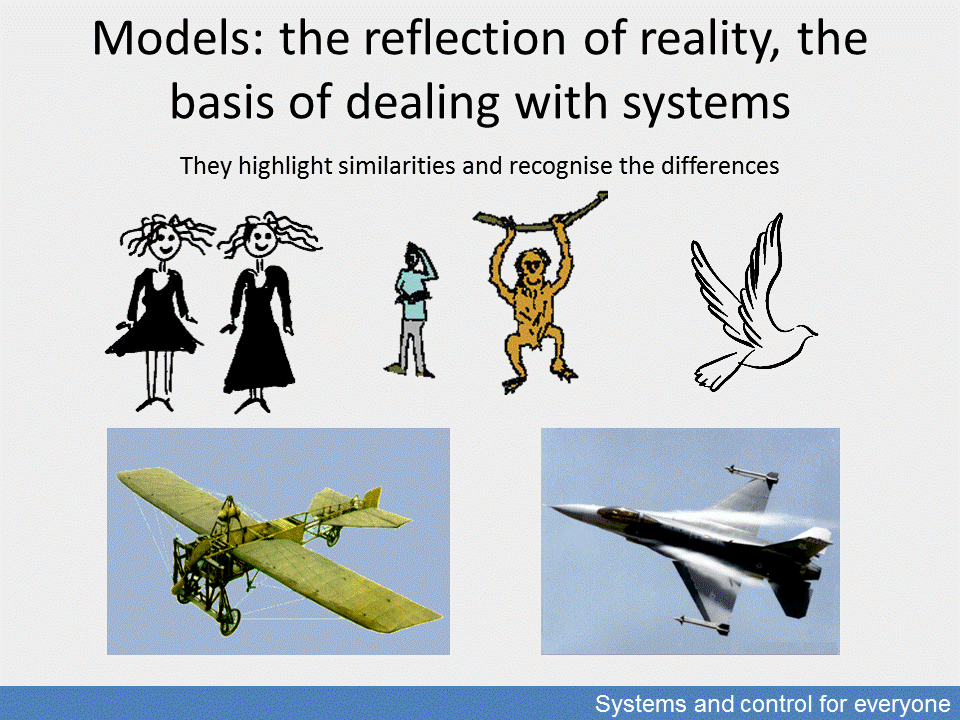

Models: similarities and differences
Models are built on the basis of recognised similarities and differences. This also follows an old recipe: Aristotle defined the two things to be recognised as genus proximum, that is the nearest species, and differentia specifica, that is the specific difference (generally used in these Latin forms, especially in the taxonomy of plants and animals). The continuous revision of results is part of the applicability of the models.
In certain applications, an aeroplane and a bird can be similar, while in other aspects, e.g. whether they are natural or artificial, creatures or machines, they are strikingly different. Certain findings in cognitive science show that model concepts and phenomena-related details in a way work similarly, that is through many kinds of associative connections in neural systems.